Executive Summary: Implementing a strategy focused on meaningful, measurable, and publicly communicated local content requirement intentions, progress, and compliance throughout all stages of infrastructure development projects is crucial for fostering economic growth, building strong community relationships, ensuring regulatory compliance, and enhancing brand reputation. This business case outlines the rationale, benefits, implementation strategies, and potential outcomes of such an approach.
1. Background and Context: Local content requirements mandate the utilization of local goods, services, workforce, and community benefit investments in infrastructure development projects. These policies are designed to promote economic development, create jobs, empower local communities, and ensure sustainable growth in regions where projects are implemented.
2. Objectives:
- Demonstrate a genuine commitment to local content requirements and community development.
- Ensure transparency, accountability, and credibility in local content compliance efforts.
- Maximize socio-economic benefits for local stakeholders, including job creation and skills development.
- Enhance regulatory compliance and minimize risks of non-compliance penalties.
- Strengthen brand reputation as a responsible corporate citizen and a partner of choice for future projects.
3. Benefits of Meaningful, Measurable, and Publicly Communicated Compliance:
- Economic Development: Stimulate local economies by supporting local businesses, creating employment opportunities, and fostering entrepreneurship.
- Social Impact: Improve living standards, promote social inclusion, and address community needs through targeted investments and partnerships.
- Stakeholder Trust: Build trust and positive relationships with local communities, governments, regulators, investors, and civil society organizations.
- Regulatory Adherence: Ensure compliance with local content requirements, mitigate legal risks, and avoid penalties or project delays.
- Brand Reputation: Enhance brand image, credibility, and market competitiveness by showcasing a commitment to sustainable development and community engagement.
4. Challenges and Risks:
- Complexity of Requirements: Local content regulations can be complex, requiring clear interpretation, implementation, and monitoring.
- Resource Availability: Ensuring the availability and quality of local goods, services, and workforce may pose logistical challenges.
- Measurement and Reporting: Establishing robust metrics, tracking mechanisms, and reporting frameworks for local content compliance can be resource-intensive.
- Stakeholder Expectations: Meeting diverse stakeholder expectations and balancing competing interests while adhering to local content requirements can be challenging.
5. Implementation Strategies:
- Early Planning: Integrate local content considerations into project planning, procurement processes, and stakeholder engagement strategies from the outset.
- Partnerships and Capacity Building: Collaborate with local businesses, organizations, and training institutions to build local workforce capacity, enhance skills development, and support entrepreneurship.
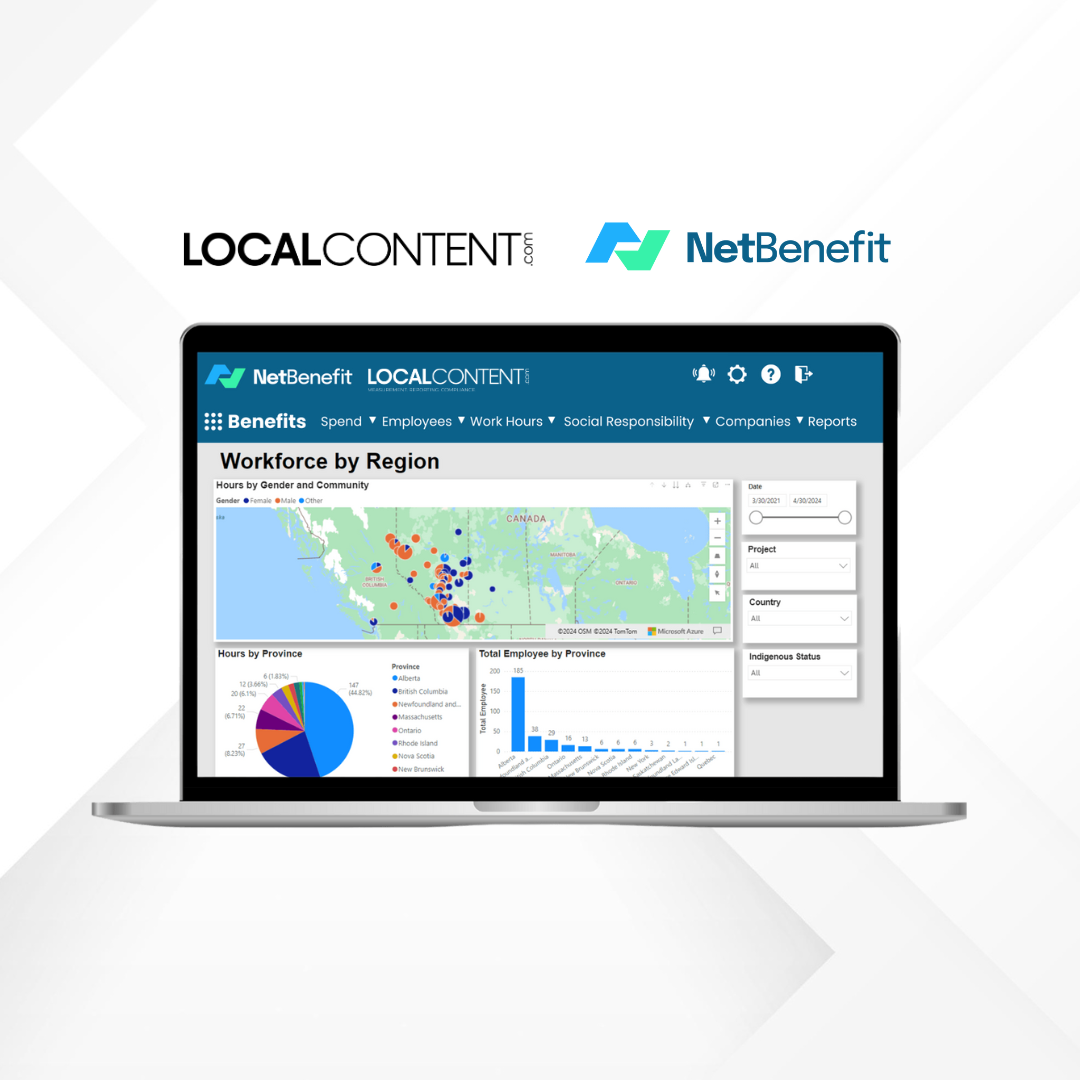
- Measurement and Monitoring: Develop clear metrics, key performance indicators (KPIs), and reporting mechanisms to track progress, achievements, and challenges related to local content compliance.
- Transparency and Communication: Communicate intentions, progress, and outcomes of local content initiatives openly and regularly through public disclosures, reports, stakeholder meetings, and social media platforms.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously evaluate and refine local content strategies based on feedback, lessons learned, and emerging best practices to optimize socio-economic impact and compliance effectiveness.
6. Cost-Benefit Analysis:
- Costs: Initial investment in capacity building, training programs, monitoring systems, reporting mechanisms, and community engagement activities.
- Benefits: Enhanced socio-economic impact, improved stakeholder relations, reduced risks of non-compliance, and strengthened brand reputation justify the upfront costs and contribute to long-term project success.
7. Performance Metrics:
- Local Content Ratio: Measure the percentage of local goods, services, workforce, and community benefit investments utilized in project implementation compared to regulatory requirements or industry standards.
- Job Creation: Track the number of local jobs created directly or indirectly through the project and assess the impact on employment levels and skills development.
- Supplier Development: Evaluate the growth, diversity, and performance of local suppliers, contractors, and partners engaged in the project.
- Community Benefits: Monitor and report on community investments, social programs, infrastructure improvements, and other initiatives that benefit local communities.
8. Potential Outcomes and Impacts:
- Economic Growth: Stimulate economic activity, promote local industry growth, and attract investment in related sectors.
- Social Development: Improve quality of life, address community needs, enhance education and healthcare facilities, and support sustainable development goals.
- Environmental Sustainability: Promote responsible resource management, adopt green technologies, and minimize environmental impacts in project execution.
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Enhance stakeholder trust, satisfaction, and engagement by delivering tangible benefits and meaningful contributions to local communities.
- Long-Term Partnerships: Build lasting relationships with local stakeholders, governments, and communities, positioning the company as a preferred partner for future projects and investments.
Conclusion: Implementing a strategy focused on meaningful, measurable, and publicly communicated local content requirement intentions, progress, and compliance is not only a regulatory requirement but also a strategic opportunity to create positive socio-economic impacts, build trust with stakeholders, and enhance brand reputation. By aligning business objectives with community needs, fostering transparency and accountability, and investing in local capacity building, companies can maximize the value of infrastructure development projects while contributing to sustainable development and inclusive growth.